By: Robert Avsec, Executive Fire Officer
Did you know?
Half of residential fire deaths result from fires reported between 11 p.m. and 7 a.m., yet only one in five residential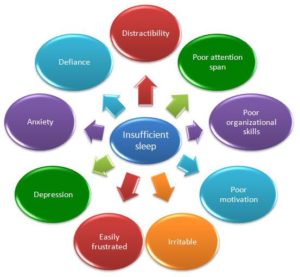 fires (20%) were reported during these hours [1].
fires (20%) were reported during these hours [1].
Those hours are also when many firefighters may not be on their “A-Game.” Why not? Because of sleep deprivation. Or because they’ve been abruptly awoken from a deep sleep cycle.
Retired Fire Chief Don Abbott is currently conducting a study on maydays across the country and has found that, for those working 48-hour shifts, the most common time for a mayday to be called is during the final 12 hours of the shift [2].
What We’re Learning About Sleep Deprivation
More than 60 percent of firefighter deaths are caused by heart attacks and traffic accidents. The results of a recent study suggest that sleep disorders may be a significant contributing factor.
In a study published in The Journal of Clinical Sleep Medicine in 2014, the researchers found that about 37 percent of firefighters in their test population screened positive for at least one sleep disorder, most of obstructive sleep apnea.
After controlling for sex, race, body mass index, smoking and other factors, the researchers found that when compared to sound sleepers, those [firefighters] with a sleep disorder were about twice as likely to have a motor vehicle crash, nod off while driving, and to have cardiovascular disease or diabetes. They were more than three times likely to suffer from depression and anxiety [3].
Firefighter Shift Schedules and Sleep Deprivation
A recent post from my fire service colleague and fellow contributor to FireRescue1.com, Sara Jahnke, entitled–Is the firefighter 48/96 shift a health hazard?–got me thinking about this topic again. I say again, because I originally wrote the following post back in 2013. So, here we are again discussing–as my original blog posted was titled–The Slow Death of the 24-Hour Tour?
Many U.S. fire and EMS organizations use some form of the 24-hour shift for around-the-clock staffing, but that may soon be changing for both employers and employees. Changes may stem from an increased awareness of sleep deprivation and its negative influences on:
- Employee and member safety;
- Critical decision-making capabilities;
- Organizational liability for actions by employees working 24-hour shifts; and
- Changing attitudes on the part of younger employees about traditional shifts.
In its study entitled Sleep-Wake Cycle: Its Physiology and Impact on Health, the National Sleep Foundation found

Firefighters from Santa Fe Springs with the Area E L.A. County Strike Team, sleep off a long night fighting fire in Julian and Wynola, on a bench in Julian Wednesday morning. Source: https://tinyurl.com/y8nvtqdy
that sleep deprivation has an adverse affect on:
- Physical health and well-being. In the past few years, investigators have found that sleep loss may have harmful consequences for immune and endocrine systems and can contribute to serious illnesses such as obesity, diabetes and hypertension.
- Cognitive performance and mood. One study showed that people who were awake for up to 19 hours scored substantially worse on performance and alertness tests than those who were legally intoxicated.
In June 2007, the International Association of Fire Chiefs (IAFC), and the United States Fire Administration (USFA), and the Oregon Health & Science University issued a 95-page report, Effects of Sleep Deprivation
on Fire Fighters and EMS Responders, detailing the negative impact of sleep deprivation on emergency services personnel. The authors of the report examined the issue of sleep deprivation in the context of EMS and firefighters.
Put simply, long work hours — defined as shifts lasting more than 10 hours — have been clearly linked to errors in tasks that require vigilance and focused alertness, such as driving an ambulance and providing patient care. ( Maggiore, W.A., Sleep Deprivation Study Details Effects of Shiftwork in EMS)
Other studies have found that after one night of total sleep deprivation, subjects scored significantly lower on tests of judgment, simple reaction time, explicit recall and inverse word reading. Also daytime alertness and memory are impaired by the loss of eight hours of sleep, especially when sleep loss is sustained over a few nights.
See Related: Why Firefighters Work 24-hour Shifts
Think about this in terms of rising EMS calls. How functional is an EMT or paramedic in an ambulance at 2 a.m. when he or she has been awake and on duty since 8 a.m.? One of the attractive features of the 24-hour shift is the firefighter’s ability to live a significant distance from the assigned duty station yet still have time for the commute. If that same medic awoke at 5:30 a.m. to arrive in time for ta tour of duty, he or she really has been awake for 20.5 hours when faced with a critical patient-care decision at 2 a.m.
The IAFC has taken a proactive stance by listing resources on its website to aid Fire & EMS organizations in taking an objective approach in dealing with sleep deprivation. These resources include a computer-based educational program, along with background information on normal sleep physiology and the health and performance effects of sleep deprivation. The IAFC also describes specific approaches for reducing the negative impact of sleep deprivation such as identifying those particularly susceptible to risks of sleep deprivation, individual mitigating strategies and work-related issues.
In light of such research, can fire and EMS managers continue to support shift schedules that, though desirable to the employee, may not be congruent with the safety interests of the employee or the public? When EMS accidents involving the operation the ambulance account for the leading cause of EMS line-of-duty deaths, can a department afford to have an employee behind the wheel whose cognitive abilities may be akin to those of the motorist taking a field sobriety test at the scene the motor-vehicle crash?
We need to be asking ourselves that question and before a plaintiff‘s attorney does it for us.
References
- National Fire Protection Association. (2017). Facts About Fire. https://www.nfpa.org/Public-Education/Campaigns/Fire-Prevention-Week/Fast-facts-about-fire
- Willing, L. Is the firefighter 48/96 shift a health hazard? FireRescue1. Retrieved From: https://www.firerescue1.com/fire-rehab/articles/223601018-Is-the-firefighter-48-96-shift-a-health-hazard/
- Bakalar, N. Firefighter Accidents are Linked to Sleep Problems. New York Times: Well Blogs. Retrieved From: https://well.blogs.nytimes.com/2014/11/13/firefighter-accidents-are-linked-to-sleep-problems/
 Fire & EMS Leader Pro The job of old firefighters is to teach young firefighters how to become old firefighters!
Fire & EMS Leader Pro The job of old firefighters is to teach young firefighters how to become old firefighters!